A Tutorial on Spark in Python Using Pyspark
Introduction
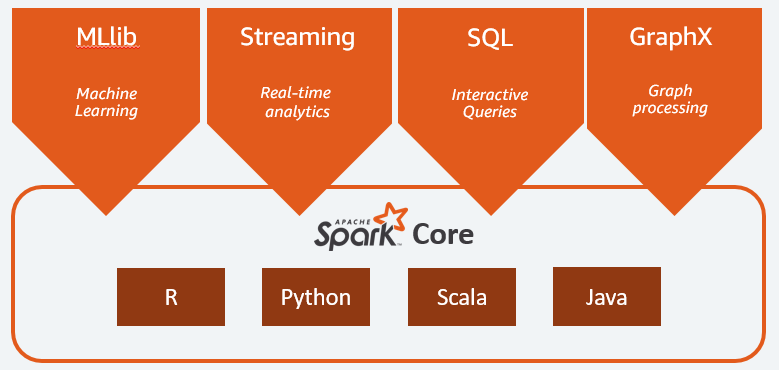
Apache Spark is a popular open-source distributed querying and processing engine. It provides flexibility and extensibility of MapReduce but at significantly higher speeds.It has quickly become the cluster computing framework for large-scale data processing and machine learning. It’s popularity has been spurred on by existing APIs in programming languages such as R, Python, Java and Scala. Spark runs on Hadoop, Mesos, standalone, or in the cloud. It can access diverse data sources including HDFS,Cassandra, HBase,NTFS, FAT, or Mac OS Extended (HFS+), and S3. Spark frameworks consist of Core Spark, Spark SQL, MLlib and ML for machine learning, GraphX and GraphFrames for graph processing, and Spark Streaming (DStreams and Structured). Spark can run run locally on a PC or laptop and can also be deployed on the cloud.It can read and write from a diverse data sources including (but not limited to) HDFS, Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase, and S3: Resilient Distributed Datasets(RDDs) apply and log transformations to the data in parallel, resulting in both increased speed and fault-tolerance. RDDs have two sets of parallel operations which are transformations and actions. Data is distributed on spark cluster as RDDs and DataFrames. Spark DataFrames behave similar to table in a relational database such storing data in columns although they are immutably distributed across clusters.
You can check which version of spark you are running by typing ‘spark-submit –version’ in the terminal
import pyspark
from pyspark import SparkContext
from operator import add
import os
First we create a SparkContext, the main object in the Spark API. This call may take a few seconds to return as it fires up a JVM under the covers.
sc = pyspark.SparkContext()
Creating RDDs
There are two ways to create an RDD in PySpark. You can parallelize a list
data = sc.parallelize(
[('Amber', 22), ('Alfred', 23), ('Skye',4), ('Albert', 12),
('Amber', 9)])
Loading Data
Parallelized Collections
rdd = sc.parallelize([('a',7),('a',2),('b',2), ('b', 3), ('c', 5)])
rdd2 = sc.parallelize([('a',2),('d',1),('b',1)])
rdd3 = sc.parallelize(range(100))
rdd4 = sc.parallelize([("a",["x","y","z"]),("b",["p", "r"])])
Reading a file in PySpark Shell
We point the context at a CSV file on disk. The result is a RDD, not the content of the file. This is a Spark transformation .
rdd = sc.textFile("green_tripdata_2016-09.csv")
Count RDD instances
rdd.count()
1162375
Transformations
Apply a function to each RDD element
rdd = sc.parallelize([('a',7),('a',2),('b',2), ('b', 3), ('c', 5)])
rdd.map(lambda x: x+(x[1],x[0])).collect()
[('a', 7, 7, 'a'),
('a', 2, 2, 'a'),
('b', 2, 2, 'b'),
('b', 3, 3, 'b'),
('c', 5, 5, 'c')]
Apply a function to each RDD element and flatten the result
The .flatMap(…) method works similarly to .map(…) but returns a flattened results instead of a list.
rdd5 = rdd.flatMap(lambda x: x+(x[1],x[0]))
rdd5.collect()
Apply a flatMap function to each (key,value) pair of rdd4 without changing the keys
rdd4.flatMapValues(lambda x: x).collect()
[('a', 'x'), ('a', 'y'), ('a', 'z'), ('b', 'p'), ('b', 'r')]
Selecting Data
Return a list with all RDD elements
rdd4.collect()
[('a', ['x', 'y', 'z']), ('b', ['p', 'r'])]
Take first 2 RDD elements
rdd.take(2)
[('a', 7), ('a', 2)]
Return sampled subset of rdd3
rdd3.sample(False, 0.15, 81).collect()
[3, 4, 13, 17, 27, 38, 41, 42, 48, 54, 56, 69, 71, 73, 76, 87, 96, 98]
Filter the RDD
The .filter(…) method allows you to select elements of your dataset that fit specified criteria.
rdd.filter(lambda x: "a" in x).collect()
[('a', 7), ('a', 2)]
.leftOuterJoin(…)
Left outer join, joins two RDDs based on the values found in both datasets, and returns records from the left RDD with records from the right one appended where the two RDDs match.
rddl = sc.parallelize([('a', 1), ('b', 4), ('c',10),('c',15)])
rddr = sc.parallelize([('a', 4), ('a', 1), ('b', '6'), ('d', 15)])
rddlj = rddl.leftOuterJoin(rddr)
rddlj.take(5)
[('b', (4, '6')),
('c', (10, None)),
('c', (15, None)),
('a', (1, 4)),
('a', (1, 1))]
The .join(…) method results in values intersect between the two RDDs ‘a’ and ‘b’.
rddj = rddl.join(rddr)
rddj.collect()
[('b', (4, '6')), ('a', (1, 4)), ('a', (1, 1))]
The .intersection(…) t returns the records that are equal in both RDDs.
rddi = rddl.intersection(rddr)
rddi.collect()
[('a', 1)]
Return distinct RDD values
rdd5.distinct().collect()
['a', 2, 3, 'b', 'c', 5, 7]
Actions
.take(…) The method returns n top rows from a single data partition
rddl.takeSample(True, 5)
[('a', 1), ('b', 4), ('b', 4), ('a', 1), ('c', 10)]
.reduce(…)
The .reduce(…) method reduces the elements of an RDD using a specified method.
rddl.map(lambda row: row[1]).reduce(lambda x, y: x + y)
30
.count()
The .count() method counts the number of elements in the RDD.
rddl.count()
4
.foreach(…)
A method that applies the same function to each element of the RDD in an iterative way.
def f(x):
print(x)
rddl.foreach(f)
Summary statistics (count, mean, stdev, max & min)
rdd3 = sc.parallelize(range(100))
rdd3.stats()
(count: 100, mean: 49.5, stdev: 28.86607004772212, max: 99.0, min: 0.0)
Maximum value of RDD elements
rdd3.max()
99
Reading Data in Data as A DataFrame
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
import pyspark.sql.functions as fn
from pyspark.sql.functions import countDistinct, avg, stddev
spark=SparkSession.builder.appName('read_sql').getOrCreate()
# Create DataFrame
dataset = spark.read.csv('/green_tripdata_2016-09.csv',header=True,inferSchema=True)
dataset.head()
Row(VendorID=2, lpep_pickup_datetime=datetime.datetime(2016, 9, 1, 0, 58, 21), lpep_dropoff_datetime=datetime.datetime(2016, 9, 1, 1, 11, 46), store_and_fwd_flag='N', RatecodeID=1, PULocationID=92, DOLocationID=82, passenger_count=1, trip_distance=3.34, fare_amount=12.5, extra=0.5, mta_tax=0.5, tip_amount=1.0, tolls_amount=0.0, ehail_fee=None, improvement_surcharge=0.3, total_amount=14.8, payment_type=1, trip_type=1)
dataset.printSchema()
root
|-- VendorID: integer (nullable = true)
|-- lpep_pickup_datetime: timestamp (nullable = true)
|-- lpep_dropoff_datetime: timestamp (nullable = true)
|-- store_and_fwd_flag: string (nullable = true)
|-- RatecodeID: integer (nullable = true)
|-- PULocationID: integer (nullable = true)
|-- DOLocationID: integer (nullable = true)
|-- passenger_count: integer (nullable = true)
|-- trip_distance: double (nullable = true)
|-- fare_amount: double (nullable = true)
|-- extra: double (nullable = true)
|-- mta_tax: double (nullable = true)
|-- tip_amount: double (nullable = true)
|-- tolls_amount: double (nullable = true)
|-- ehail_fee: string (nullable = true)
|-- improvement_surcharge: double (nullable = true)
|-- total_amount: double (nullable = true)
|-- payment_type: integer (nullable = true)
|-- trip_type: integer (nullable = true)
Obtain summary statistics in the DataFrame
dataset.describe().show()
+-------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------------+-------------------+------------------+-------------------+---------+---------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------------+
|summary| VendorID|store_and_fwd_flag| RatecodeID| PULocationID| DOLocationID| passenger_count| trip_distance| fare_amount| extra| mta_tax| tip_amount| tolls_amount|ehail_fee|improvement_surcharge| total_amount| payment_type| trip_type|
+-------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------------+-------------------+------------------+-------------------+---------+---------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------------+
| count| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 0| 1162373| 1162373| 1162373| 1162372|
| mean|1.7937538122444345| null|1.0898463746146891|114.97562572427267|129.92474446670732|1.3436676522940572|2.8324054670919048|12.372125195612776| 0.3620072902588068| 0.486971910049528|1.2213373676092194|0.11974514204993575| null| 0.29226909090311565|14.897254091427396|1.5246844171363236| 1.0209373591242734|
| stddev|0.4046094890534029| null|0.5887798694615354| 76.68393912971331| 77.26233287188323| 1.00406748105953|2.9784182350530366|10.785951837515272|0.38517483519212703|0.08503704304060737| 2.443655817645052| 0.9357983193563992| null| 0.050786660285064324|12.219191909782575|0.5246788914296506|0.14317473154390079|
| min| 1| N| 1| 1| 1| 0| 0.0| -300.09| -4.5| -0.5| -40.0| -50.0| null| -0.3| -300.09| 1| 1|
| max| 2| Y| 99| 265| 265| 9| 227.44| 3361.0| 4.5| 0.5| 450.0| 150.0| null| 0.3| 3362.8| 5| 2|
+-------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------------+-------------------+------------------+-------------------+---------+---------------------+------------------+------------------+-------------------+
To obtain the summary output in a nicer format , we can use the function toPandas to display the output similar to a pandas dataframe
# in a nicer format
dataset.describe().toPandas()
| summary | VendorID | store_and_fwd_flag | RatecodeID | PULocationID | DOLocationID | passenger_count | trip_distance | fare_amount | extra | mta_tax | tip_amount | tolls_amount | ehail_fee | improvement_surcharge | total_amount | payment_type | trip_type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | count | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 0 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162373 | 1162372 |
| 1 | mean | 1.7937538122444345 | None | 1.0898463746146891 | 114.97562572427267 | 129.92474446670732 | 1.3436676522940572 | 2.8324054670919048 | 12.372125195612776 | 0.3620072902588068 | 0.486971910049528 | 1.2213373676092194 | 0.11974514204993575 | None | 0.29226909090311565 | 14.897254091427396 | 1.5246844171363236 | 1.0209373591242734 |
| 2 | stddev | 0.4046094890534029 | None | 0.5887798694615354 | 76.68393912971331 | 77.26233287188323 | 1.00406748105953 | 2.9784182350530366 | 10.785951837515272 | 0.38517483519212703 | 0.08503704304060737 | 2.443655817645052 | 0.9357983193563992 | None | 0.050786660285064324 | 12.219191909782575 | 0.5246788914296506 | 0.14317473154390079 |
| 3 | min | 1 | N | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.0 | -300.09 | -4.5 | -0.5 | -40.0 | -50.0 | None | -0.3 | -300.09 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | max | 2 | Y | 99 | 265 | 265 | 9 | 227.44 | 3361.0 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 450.0 | 150.0 | None | 0.3 | 3362.8 | 5 | 2 |
To obtain the column names
dataset.columns
['VendorID',
'lpep_pickup_datetime',
'lpep_dropoff_datetime',
'store_and_fwd_flag',
'RatecodeID',
'PULocationID',
'DOLocationID',
'passenger_count',
'trip_distance',
'fare_amount',
'extra',
'mta_tax',
'tip_amount',
'tolls_amount',
'ehail_fee',
'improvement_surcharge',
'total_amount',
'payment_type',
'trip_type']
Sorting trip_distance(OrderBy) and toPandas:
#limit displays the top 10 after sorting
dataset.orderBy('trip_distance',ascending = False).limit(10).toPandas()[['VendorID', 'trip_distance','fare_amount','tip_amount','passenger_count','trip_type']]
| VendorID | trip_distance | fare_amount | tip_amount | passenger_count | trip_type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 227.44 | 965.5 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 | 140.86 | 599.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 | 138.24 | 405.5 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | 2 | 133.85 | 630.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 | 128.40 | 326.0 | 0.0 | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 | 124.48 | 316.5 | 0.0 | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | 2 | 122.30 | 339.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | 2 | 120.26 | 626.0 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 8 | 2 | 119.77 | 611.5 | 0.0 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | 2 | 97.91 | 361.0 | 1.0 | 1 | 1 |
dataset.filter('trip_distance < 500').select(['trip_distance','VendorID', 'passenger_count','tip_amount','passenger_count','trip_type']).show(5)
+-------------+--------+---------------+----------+---------------+---------+
|trip_distance|VendorID|passenger_count|tip_amount|passenger_count|trip_type|
+-------------+--------+---------------+----------+---------------+---------+
| 3.34| 2| 1| 1.0| 1| 1|
| 3.78| 2| 2| 0.0| 2| 1|
| 4.84| 2| 1| 0.0| 1| 1|
| 28.26| 2| 1| 30.08| 1| 1|
| 3.5| 2| 1| 2.66| 1| 1|
+-------------+--------+---------------+----------+---------------+---------+
only showing top 5 rows
dataset.filter((dataset['total_amount'] > 200) & ~(dataset['total_amount'] < 200)).select(['total_amount','trip_distance','VendorID', 'passenger_count']).show(5)
+------------+-------------+--------+---------------+
|total_amount|trip_distance|VendorID|passenger_count|
+------------+-------------+--------+---------------+
| 464.8| 0.0| 2| 5|
| 202.8| 2.0| 1| 5|
| 210.8| 42.11| 2| 1|
| 201.0| 36.24| 2| 1|
| 233.8| 0.0| 2| 5|
+------------+-------------+--------+---------------+
only showing top 5 rows
dataset.select(['total_amount','trip_distance','VendorID', 'passenger_count']).groupBy('VendorID').mean().show()
+--------+------------------+------------------+-------------+--------------------+
|VendorID| avg(total_amount)|avg(trip_distance)|avg(VendorID)|avg(passenger_count)|
+--------+------------------+------------------+-------------+--------------------+
| 1|14.590393392699324| 2.792817485974092| 1.0| 1.1948943625252884|
| 2|14.976987691834658| 2.842691868316733| 2.0| 1.3823243785753458|
+--------+------------------+------------------+-------------+--------------------+
from pyspark.sql.functions import mean
dataset.select(mean('total_amount')).collect()
[Row(avg(total_amount)=14.897254091427396)]
dataset.select(mean(dataset['total_amount'])).collect()
[Row(avg(total_amount)=14.897254091427396)]
find distinct rows of VendorID
dataset.select('VendorID').distinct().rdd.map(lambda r: r[0]).collect()
[1, 2]
dataset.toPandas()['VendorID'].unique()
array([2, 1])
dataset.select('VendorID').distinct().show()
+--------+
|VendorID|
+--------+
| 1|
| 2|
+--------+
Count distinct values of VendorIG
dataset.select(countDistinct('VendorID')).show()
+------------------------+
|count(DISTINCT VendorID)|
+------------------------+
| 2|
+------------------------+
dataset.select('RatecodeID').distinct().show()
+----------+
|RatecodeID|
+----------+
| 1|
| 6|
| 3|
| 5|
| 4|
| 2|
| 99|
+----------+
dataset.select(avg('total_amount').alias('Average Total_amount')).show()
+--------------------+
|Average Total_amount|
+--------------------+
| 14.897254091427396|
+--------------------+
Handling Missing Values
df_miss = spark.createDataFrame([
(1, 143.5, 5.6, 28, 'M', 100000),
(2, 167.2, 5.4, 45, 'M', None),
(3, None , 5.2, None, None, None),
(4, 144.5, 5.9, 33, 'M', None),
(5, 133.2, 5.7, 54, 'F', None),
(6, 124.1, 5.2, None, 'F', None),
(7, 129.2, 5.3, 42, 'M', 76000),
], ['id', 'weight', 'height', 'age', 'gender', 'income'])
df_miss.toPandas()
| id | weight | height | age | gender | income | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 143.5 | 5.6 | 28.0 | M | 100000.0 |
| 1 | 2 | 167.2 | 5.4 | 45.0 | M | NaN |
| 2 | 3 | NaN | 5.2 | NaN | None | NaN |
| 3 | 4 | 144.5 | 5.9 | 33.0 | M | NaN |
| 4 | 5 | 133.2 | 5.7 | 54.0 | F | NaN |
| 5 | 6 | 124.1 | 5.2 | NaN | F | NaN |
| 6 | 7 | 129.2 | 5.3 | 42.0 | M | 76000.0 |
To find the number of missing observations per row.
df_miss.rdd.map(
lambda row: (row['id'], sum([c == None for c in row]))
).collect()
[(1, 0), (2, 1), (3, 4), (4, 1), (5, 1), (6, 2), (7, 0)]
select rows with missing values
df_miss.where('id == 3').show()
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| id|weight|height| age|gender|income|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| 3| null| 5.2|null| null| null|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
percentage of missing observations we see in each column
df_miss.agg(*[
(1 - (fn.count(c) / fn.count('*'))).alias(c + '_missing')
for c in df_miss.columns
]).show()
+----------+------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+
|id_missing| weight_missing|height_missing| age_missing| gender_missing| income_missing|
+----------+------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+
| 0.0|0.1428571428571429| 0.0|0.2857142857142857|0.1428571428571429|0.7142857142857143|
+----------+------------------+--------------+------------------+------------------+------------------+
Drop both income and weight columns
df_miss_no_weight = df_miss.select([c for c in df_miss.columns if c != 'weight'])
df_miss_no_weightincome=df_miss_no_weight.select([c for c in df_miss_no_weight.columns if c != 'income'])
df_miss_no_weightincome.show()
+---+------+----+------+
| id|height| age|gender|
+---+------+----+------+
| 1| 5.6| 28| M|
| 2| 5.4| 45| M|
| 3| 5.2|null| null|
| 4| 5.9| 33| M|
| 5| 5.7| 54| F|
| 6| 5.2|null| F|
| 7| 5.3| 42| M|
+---+------+----+------+
We can drop the observations by using the .dropna(…) method.
df_miss_no_weightincome.dropna(thresh=3).show()
+---+------+----+------+
| id|height| age|gender|
+---+------+----+------+
| 1| 5.6| 28| M|
| 2| 5.4| 45| M|
| 4| 5.9| 33| M|
| 5| 5.7| 54| F|
| 6| 5.2|null| F|
| 7| 5.3| 42| M|
+---+------+----+------+
To impute a mean, median or other calculated value you need to first calculate the value, create a dict with such values, and then pass it to the .fillna(…) method.
df_miss_no_income = df_miss.select([c for c in df_miss.columns if c != 'income'])
means = df_miss_no_income.agg(
*[fn.mean(c).alias(c) for c in df_miss_no_income.columns if c != 'gender']
).toPandas().to_dict('records')[0]
means['gender'] = 'missing'
df_miss_no_income.fillna(means).show()
+---+------------------+------+---+-------+
| id| weight|height|age| gender|
+---+------------------+------+---+-------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M|
| 3|140.28333333333333| 5.2| 40|missing|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2| 40| F|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M|
+---+------------------+------+---+-------+
df_miss.toPandas()
| id | weight | height | age | gender | income | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 143.5 | 5.6 | 28.0 | M | 100000.0 |
| 1 | 2 | 167.2 | 5.4 | 45.0 | M | NaN |
| 2 | 3 | NaN | 5.2 | NaN | None | NaN |
| 3 | 4 | 144.5 | 5.9 | 33.0 | M | NaN |
| 4 | 5 | 133.2 | 5.7 | 54.0 | F | NaN |
| 5 | 6 | 124.1 | 5.2 | NaN | F | NaN |
| 6 | 7 | 129.2 | 5.3 | 42.0 | M | 76000.0 |
Drop all rows with missing values
df_miss.na.drop().show()
+---+------+------+---+------+------+
| id|weight|height|age|gender|income|
+---+------+------+---+------+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|100000|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M| 76000|
+---+------+------+---+------+------+
Drop missing values based on gender column
df_miss.na.drop(subset="gender").show()
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| id|weight|height| age|gender|income|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|100000|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M| null|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M| null|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F| null|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2|null| F| null|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M| 76000|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
fill numeric missing values with 0
df_miss.na.fill(0).show()
+---+------+------+---+------+------+
| id|weight|height|age|gender|income|
+---+------+------+---+------+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|100000|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M| 0|
| 3| 0.0| 5.2| 0| null| 0|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M| 0|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F| 0|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2| 0| F| 0|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M| 76000|
+---+------+------+---+------+------+
fill character missing values
df_miss.na.fill('fill value').show()
+---+------+------+----+----------+------+
| id|weight|height| age| gender|income|
+---+------+------+----+----------+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|100000|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M| null|
| 3| null| 5.2|null|fill value| null|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M| null|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F| null|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2|null| F| null|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M| 76000|
+---+------+------+----+----------+------+
df_miss.na.fill('no name', subset = 'weight').show()
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| id|weight|height| age|gender|income|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
| 1| 143.5| 5.6| 28| M|100000|
| 2| 167.2| 5.4| 45| M| null|
| 3| null| 5.2|null| null| null|
| 4| 144.5| 5.9| 33| M| null|
| 5| 133.2| 5.7| 54| F| null|
| 6| 124.1| 5.2|null| F| null|
| 7| 129.2| 5.3| 42| M| 76000|
+---+------+------+----+------+------+
Dates and Timestamps
from pyspark.sql.functions import (dayofmonth, hour, dayofyear, month,
year, weekofyear, format_number, date_format)
lpep_pickup_datetime: timestamp (nullable = true)
|-- lpep_dropoff_datetime: timestamp (nullable = true)
dataset.select(dayofmonth(dataset['lpep_dropoff_datetime'])).show(5)
+---------------------------------+
|dayofmonth(lpep_dropoff_datetime)|
+---------------------------------+
| 1|
| 1|
| 1|
| 1|
| 1|
+---------------------------------+
only showing top 5 rows
dataset.select(hour(dataset['lpep_dropoff_datetime'])).show(5)
+---------------------------+
|hour(lpep_dropoff_datetime)|
+---------------------------+
| 1|
| 1|
| 0|
| 1|
| 0|
+---------------------------+
only showing top 5 rows
dataset.select(month(dataset['lpep_dropoff_datetime'])).show(5)
+----------------------------+
|month(lpep_dropoff_datetime)|
+----------------------------+
| 9|
| 9|
| 9|
| 9|
| 9|
+----------------------------+
only showing top 5 rows